GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
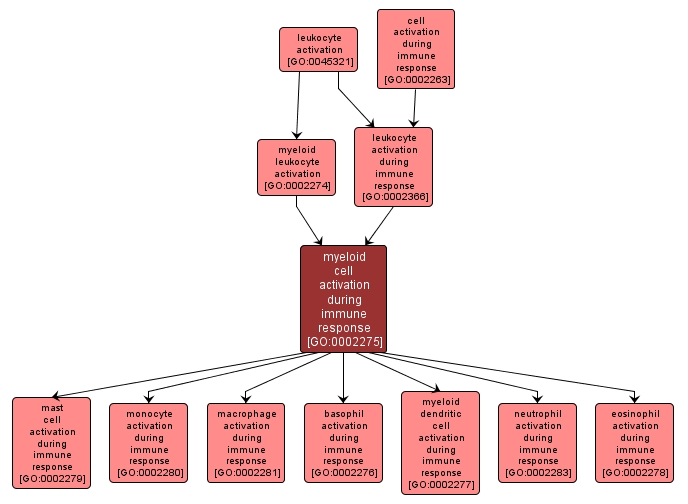
myeloid cell activation during immune response |
| Acc: |
GO:0002275 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
A change in the morphology or behavior of a myeloid cell resulting from exposure to an activating factor such as a cellular or soluble ligand, leading to the initiation or perpetuation of an immune response. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|