| Desc: |
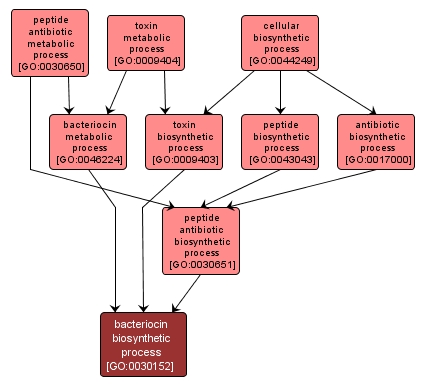
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a bacteriocin, any of a heterogeneous group of polypeptide antibiotics that are secreted by certain bacterial strains and are able to kill cells of other susceptible (frequently related) strains after adsorption at specific receptors on the cell surface. They include the colicins, and their mechanisms of action vary. |