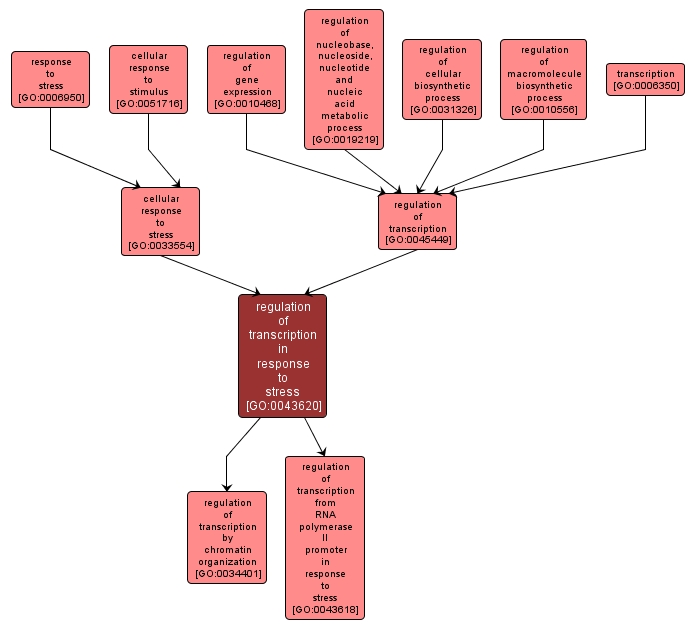
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
regulation of transcription in response to stress |
| Acc: |
GO:0043620 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Modulation of the frequency, rate or extent of transcription as a result of a stimulus indicating the organism is under stress. The stress is usually, but not necessarily, exogenous (e.g. temperature, humidity, ionizing radiation). |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|