GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
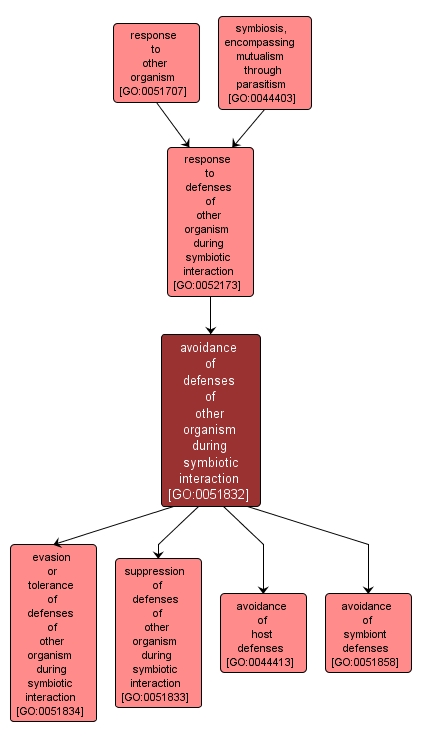
avoidance of defenses of other organism during symbiotic interaction |
| Acc: |
GO:0051832 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Any process, either constitutive or induced, by which an organism evades, minimizes, or suppresses the effects of a second organism's defense(s), where the two organisms are in a symbiotic interaction. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|