| Desc: |
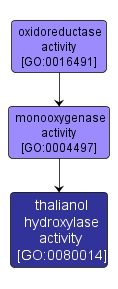
Catalysis of the addition of a hydroxyl group to thalianol ((13R,14R,17E)-podioda-8,17,21-trien-3beta-ol) to create thalian-diol ((13R,14R,17E)-podioda-8,17,21-trien-3beta, ?-diol). Several thalian-diol isomers may be created by the same enzyme because the hydroxyl group may be attached at one of several different available carbons in ring B or C of thalianol (as indicated by the ''?''). |