GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
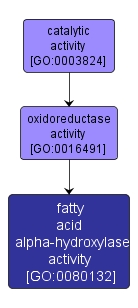
fatty acid alpha-hydroxylase activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0080132 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the conversion of a fatty acid to an alpha-hydroxylated fatty acid. A hydroxyl group is added to the second carbon, counted from the carboxyl end, of a fatty acid chain. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|